The electric utility sector is undergoing an unprecedented energy transition that requires reducing carbon emissions, promoting decentralization, and increasing the digitalization of workflows. These changes significantly affect electrical distribution, especially with the rise of Behind-the-Meter (BTM) systems. Utilities' future success hinges on their ability to address these challenges holistically and cost-effectively.
Utilities must implement automated work procedures that use shared data and adaptable tools throughout the life of the electric grid. Work process digitalization instantaneously gives field staff access to work order data and enables monitoring of back-office work progress in real-time. Field crews equipped with these digital technologies are necessary to optimize the operation of modern electrical distribution systems.
The network lifecycle
The electrical distribution network lifecycle has four phases: Plan, Build, Operate, and Respond. Each phase requires process optimization and integration with systems like a Geographic Information System (GIS), Workforce Management System (WMS), Outage Management System (OMS) as well as the ability to access them from the field. Mobile apps support the network lifecycle by digitalizing the process of sharing data and optimizing previously manual data-handling processes, which enhances productivity and cuts costs.
![]()
Plan your network - The “Plan” phase boosts situational awareness through mobile apps and their ability to share real-time data with operational systems. The network is updated dynamically using digital design tools that optimize fieldwork processes. Mobile apps enable field crews to digitally perform staking, field design, construction estimates, and drawing mark-ups, making the process more efficient and productive.
Build your network - In the "Build" phase, mobile apps improve data quality for construction teams and streamline the preparation of as-built drawings. Field crews also use mobile apps to record updated field data for engineering and management. This accelerates the build process and better manages changes in a dynamic work environment.
Operate and maintain your network - In the "Operate and maintain" phase, field crews use mobile apps to receive geo-enabled work orders to shorten response times. Smart forms are customizable for task and workforce planning and may be integrated with Advanced Distribution Management Systems (ADMS) and Outage Management Systems (OMS). Field crews can also update as-built drawings, GIS databases, and asset inspection reports online and offline, enabling efficient network operation and maintenance.
Respond and repair your network - The “Respond and repair” phase uses mobile applications to accelerate service restoration without compromising field crew safety. For example, field crews can view affected areas on a tablet, which facilitates faster workforce activation during disaster response incidents. Further, mobile apps allow field crews to update system status in real-time. In return, headquarters can also keep field crews informed of any changes in network or environmental conditions.

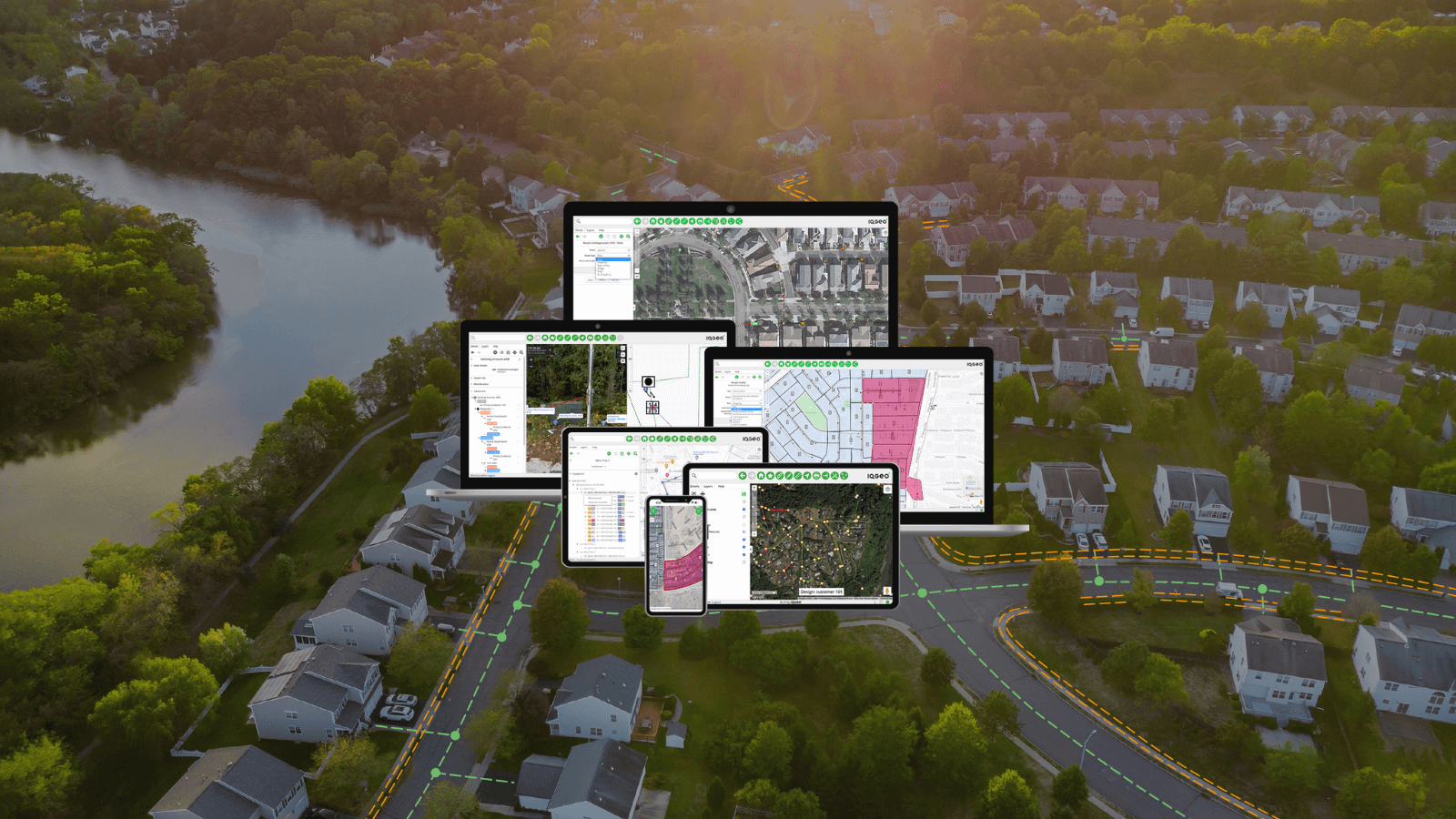
IQGeo's modern geospatial software
Business case for mobile applications
Mobile applications are essential during the entire network lifecycle, particularly for enabling grid modernization projects and decision-making during design, construction, maintenance, and operations. IQGeo’s mobility software delivers measurable and compelling business value across the five critical operational benchmarks, summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 - Five critical operational benchmarks for electrical utilities deploying mobile applications.
| Real time communication | Streamlined workflows | Improved data accuracy | Enhanced safety measures | Optimized asset management |
|
Mobile apps allow real-time communication between field crews and headquarters to improve team coordination. |
Mobile apps help field crews to remotely access work orders and geospatial data to quickly locate assets. |
Mobile apps reduce errors in manual data entry and improve documentation of field tasks. |
Mobile apps can include real-time asset location and environmental protocols to enable field crews to safely respond to emergencies. |
Mobile apps give field crews current asset information, maintenance schedules, and historical data to make informed decisions. |
Utilities migrate to mobility solutions
Many utilities have heavily invested in mobile applications as they significantly enhance productivity, optimize resource use, improve the field user experience, and ensure the reliable delivery of services to customers. The following case studies briefly illustrate different approaches to mobile geospatial applications:
Case study 1: A northwest U.S. utility serving one million customers relies on mobile geospatial solutions for electrical distribution operations. Field crews use IQGeo on iPads to access and update grid data in real time, reducing delays in as-built updates from months to immediate on-site entries. The utility envisions a comprehensive “Super App” that integrates real-time circuit data, emergency response, and Distributed Energy Resources (DER) functions to improve efficiency, safety, and decision-making.
Case study 2: A northeastern U.S. utility is upgrading its interconnection processes to achieve 50% renewable energy by 2030, focusing on DERs, energy storage, and Electric Vehicle (EV) charging. Field crews utilize iPads for the purpose of asset inspection and data collection, thereby enhancing maintenance procedures. Furthermore, the organization integrates drones with mobile applications to facilitate the process of data collection and mapping, thereby streamlining operations and optimizing efficiency.
Case study 3: A utility department in a California city is using a mobile GIS solution to work more efficiently and share asset data with other departments. The project aims to help the utility make better decisions by giving its staff real-time access to location-based data on their mobile devices.
Field crews equipped with mobile devices running IQGeo allow as-built updates to be completed before leaving the job site.
Empower grid modernization with a mobile geospatial strategy
Utilities must fully embrace the digital transformation of their assets and workforce to remain competitive. Mobile applications will have a crucial role in digitalizing their workflows.
By harnessing the power of mobile technology, utilities can enhance communication, streamline workflows, and optimize operations.
Access the comprehensive research paper “Empower grid modernization with mobile geospatial strategy,” which explores the field experiences of utilities that have successfully implemented IQGeo's geospatial solutions. 
Don't miss the webinar, “Grid modernization depends on geospatial mobility,” featuring industry experts from Krishnan & Associates, exclusive case studies, and live demonstrations of mobile application software in action.
View webinar >>>

Managing Director, Krishnan & Associates
Similar articles:

 Previous
Previous